NRAS is detected as a mutational cancer driver in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
NRAS reports in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Cancer type details
| Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
|---|
|
Cohorts
9
Samples 661 Mutations 295,755 Driver genes 71 |
Gene details
| NRAS |
|---|
|
Gene ID
ENSG00000213281
Transcript ID ENST00000369535 Protein ID ENSP00000358548 |
|
Cohorts where is driver
6
Mutated samples 45 Mutated samples (%) 6.81 Mutations 55 |
| Known driver True |
Method signals per Cohort
| Cohort | Methods | Samples | Samples (%) |
|---|
ClustL
HotMAPS
smRegions
Clustered Mutations
CBaSE dNdScv Recurrent Mutations
FML Functional Mutations
MutPanning Tri-nucleotide specific bias
combination Combination
CBaSE dNdScv Recurrent Mutations
FML Functional Mutations
MutPanning Tri-nucleotide specific bias
combination Combination
In-silico saturation mutagenesis
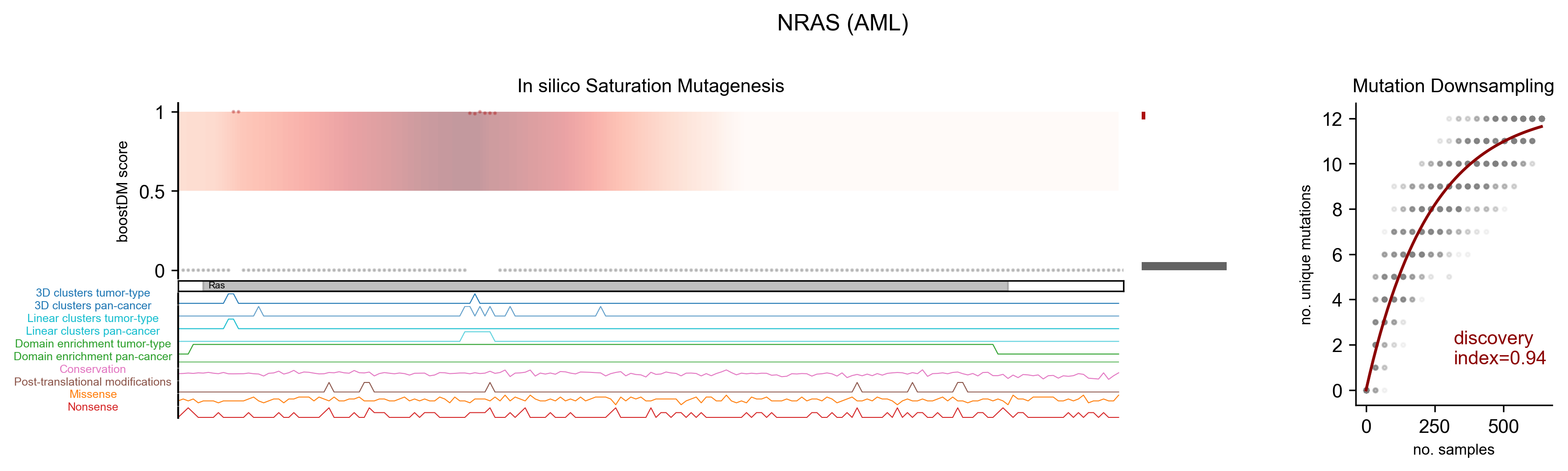
In-silico saturation mutagenesis Left: In silico saturation mutagenesis of all coding variants represented in their relative position of the gene coding sequence. Relevant functional protein domains are represented within each gene body. Potential driver mutations appear in red and potential passenger mutations in gray. The concentration of driver mutations at different regions of the protein is represented as a density. The vertical bar plot shows the frequency bins of boostDM scores. Right: For each random subsample of the tumor type cohort, the number of unique mutations mapping to the gene can be counted. The bend of the best fitting curve to the subsampling data is informative of how close the current pool of mutations is from representing all the possible mutations in this gene-tumor type context..
| Model | Mutations | Driver mutations | Driver mutations (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AML (Acute Myeloid Leukemia) | 2146 | 43 | 2.00 |
Observed mutations in tumors
The mutations needle plot shows the distribution of the observed
mutations along the protein sequence.
| Mutation (GRCh38) | Protein Position | Samples | Samples (%) | Consequence | Driver | Driver score |
|---|